Headlands Primary School | Design Technology Narrative
The Design Technology curriculum prepares children to deal with tomorrow’s rapidly changing world. It encourages children to become independent, creative problem solvers and thinkers as individuals and part of a team. It enables them to identify needs and opportunities and to respond to them by developing a range of ideas and by making products and systems. Through the study of Design and Technology, they combine practical skills with an understanding of aesthetic, social and environmental issues, as well as functions and industry. This allows them to reflect on and evaluate past and present technology, its uses, and impacts.
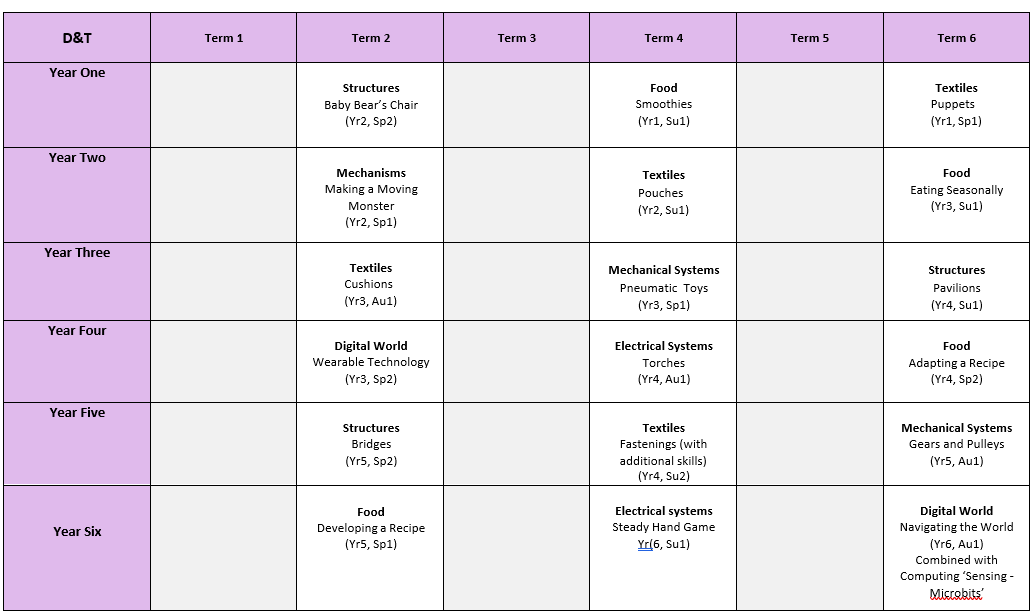
At Headlands Primary School, Design Technology is taught in all year groups every alternate term. The curriculum focuses on the progression of high dividend concepts: designing, making, and communicating; materials, components, and tools; structures, health and safety, electrical and electronics, mechanics, textiles, food and controlled vehicles.
The national curriculum for Design and Technology aims to ensure that all children:
· develop the creative, technical, and practical expertise need to perform everyday tasks confidently and to participate successfully in an increasingly
technological world
· build and apply a repertoire of knowledge, understanding and skills to design and make high-quality prototypes and products for a wide range of users
· critique, evaluate and test their ideas and products and the work of others
· understand and apply the principles of nutrition and learn how to cook
Children design products with a purpose in mind and an intended user of the products. Food technology is implemented across the school with children developing an understanding of where food comes from, the importance of a varied and healthy diet and how to prepare this.
Design and Technology is an inspiring, rigorous, and practical subject, requiring creativity, resourcefulness, and imagination. Children design and make products that solve real and relevant problems within a variety of contexts. It is cross - curricular and draws upon subject knowledge and skills within Mathematics, Science, History, Computing and Art. Children learn to take risks, be reflective, innovative, enterprising, and resilient.
Each year, the children will study a designer in depth to understand their perspectives on how past technologies have influenced their work and innovations for the future. (Year 1- Zaha Hadid (structures, Year 2 James Dyson (mechanics), Year 3 Isambard Kingdom Brunel (structures), Year 4 Lisa Call (textiles), Year 5 William Morris (textiles), Year 6 Marcus Samuelson (food).
When designing and making, children will be taught the disciplinary knowledge of designing, making and evaluating.
| At Key Stage 1 | At Key Stage 2 | |
| Designing | Design purposeful, functional, appealing products for themselves and other users based on design criteria. Generate, develop, model and communicate their ideas through talking, drawing, templates, mock-ups and, where appropriate, information and communication technology. |
use research and develop design criteria to inform the design of innovative, functional, appealing products that are fit for purpose, aimed at individuals or groups |
| Making | Select from and use a range of tools and equipment to perform practical tasks, (or example, cutting, shaping, joining and finishing). Select from and use a wide range of materials and components, including construction materials, textiles and ingredients, according to their characteristics. |
select from and use a wider range of tools and equipment to perform practical tasks, such as cutting, shaping, joining, and finishing, accurately |
| Evaluating | Explore and evaluate a range of existing products. Evaluate their ideas and products against design criteria | Investigate and analyse a range of existing products. Evaluate their ideas and products against their own design criteria and consider the views of others to improve their work. Understand how key events and individuals in design and technology have helped shape the world. |
| Technical knowledge | Build structures, exploring how they can be made stronger, stiffer and more stable. Explore and use mechanisms, (for example levers, sliders, wheels and axles), in their products. | Apply their understanding of how to strengthen, stiffen and reinforce more complex structures. Understand and use mechanical systems in their products, (for example as gears, pulleys, cams, levers and linkages). Understand and use electrical systems in their products, (for example series circuits incorporating switches, bulbs, buzzers and motors). To apply their understanding of computing to programme, monitor and control their products. |
Technical vocabulary will be promoted in every lesson.
Food Technology
As part of their work with food, children should be taught how to cook and apply the principles of nutrition and healthy eating. Instilling a love of cooking in children will also open a door to one of the great expressions of human creativity. Learning how to cook is a crucial life skill that enables children to feed themselves and others affordably and well, now and in later life.
At Key Stage 1, children will be taught to:
· use the basic principles of a healthy and varied diet to prepare dishes
· understand where food comes from.
At Key Stage 2, children will be taught to:
· understand and apply the principles of a healthy and varied diet
· prepare and cook a variety of predominantly savory dishes using a range of cooking techniques
. to understand seasonality and know where and how a variety of ingredients are grown, reared, caught and processed
Design Technology Long Term Plan